Tracking SMART table status before/after imaging
Being able to evaluate the drive’s state before it has exhausted its resources can make all the difference between a case won or a case lost in a court of law.
SMART table is a valuable source of information about a hard drive’s health. SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) provides stats of a drive’s operation, thus helping predict its future failure.
Making a definitive conclusion based on the indices in SMART table is not easy: not all parameters are critical, it is usually a combination of bad values of a few parameters that point to a trouble, time factor plays a role too (how fast has the state of the drive been deteriorating).
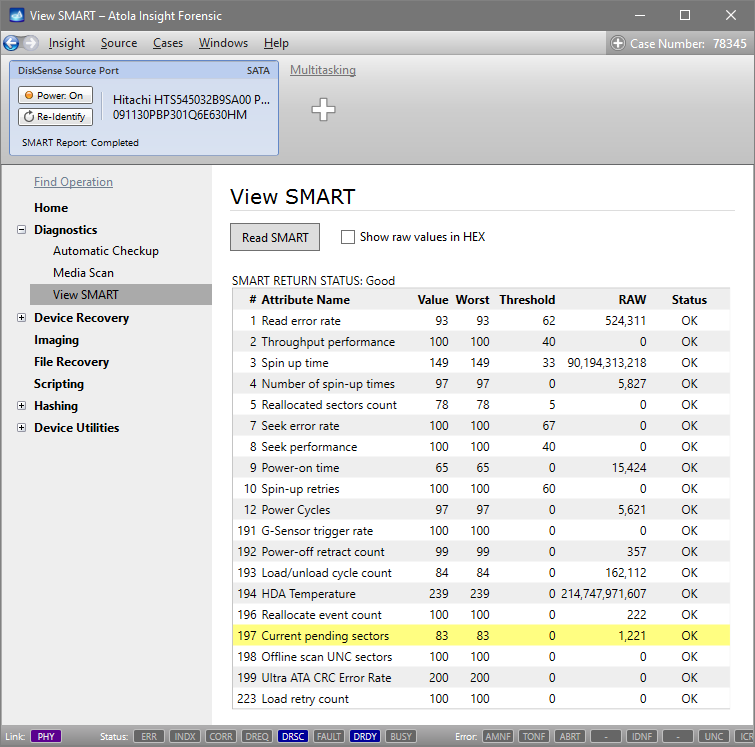
View SMART table
To view SMART table of a drive:
- In the sidebar, go to Diagnostics > View SMART.
- Click Read SMART.
SMART table attributes may differ depending on the drive manufacturer. The most critical attributes are:
- Reallocated sectors count
- Current pending sector count
- Uncorrectable sector count
When RAW value of any of these attributes is greater than zero, Insight highlights it in yellow.
The worse the values, especially in these critical attributes, the more carefully the drive needs to be treated.
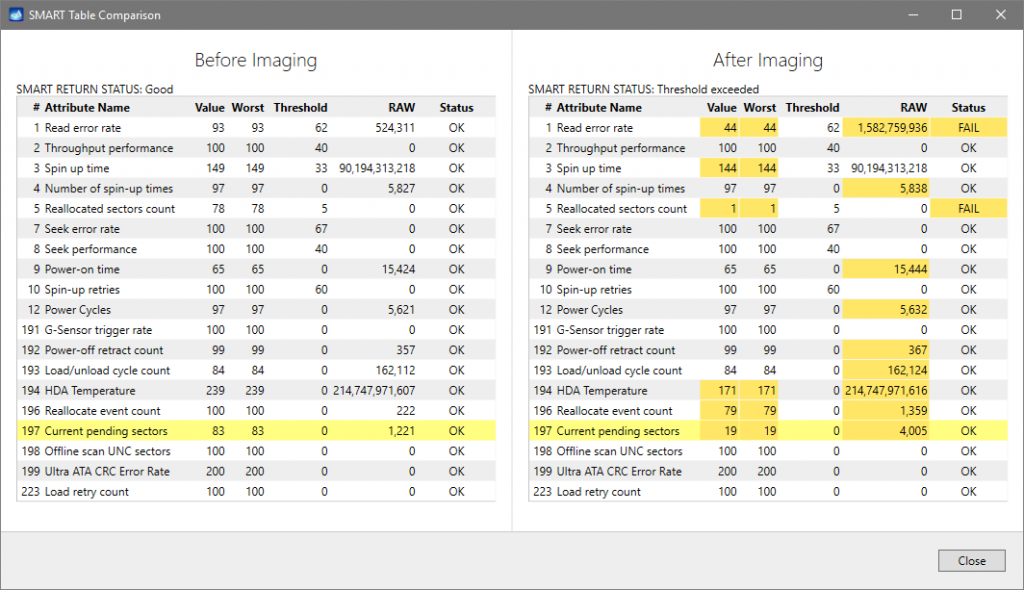
Compare SMART tables
To keep track of the changes occurring to the attributes of the SMART table, Insight records SMART table indices prior and after each imaging session.
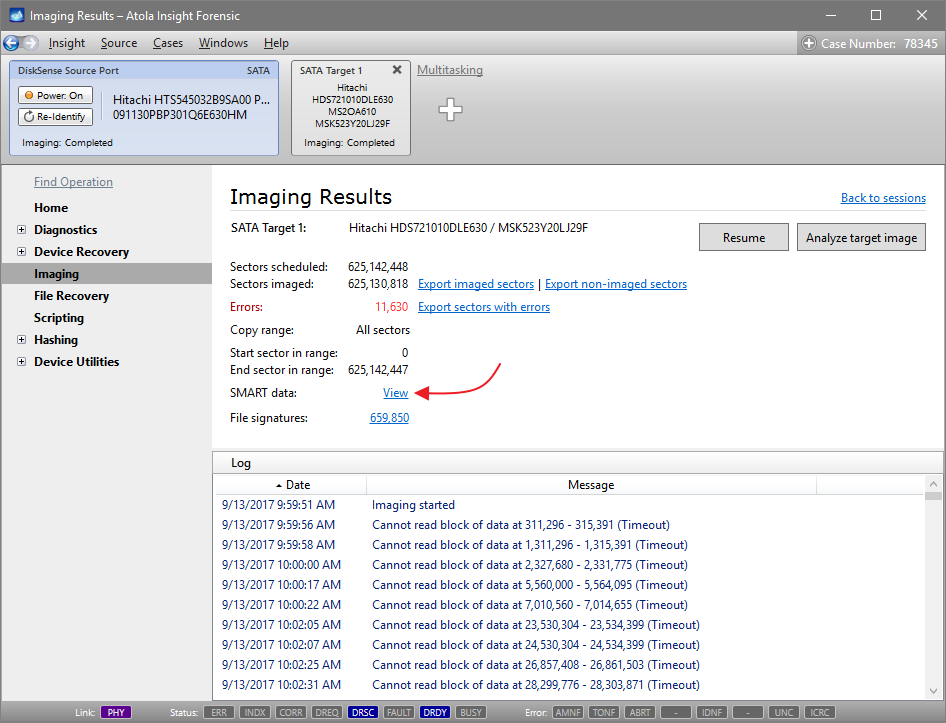
To open both SMART tables for side-by-side comparison:
- After the imaging is completed, check the Imaging Results.
- In SMART data line, click the View link.
By comparing the two tables, operator can evaluate whether the health of a drive has been deteriorating throughout the imaging session and thus assess how quickly its health has been getting worse.
Whenever you need to evaluate how the state of the drive has been changing long-term, you can go to previous imaging sessions and look up SMART table. Insight stores this information in its case management system.