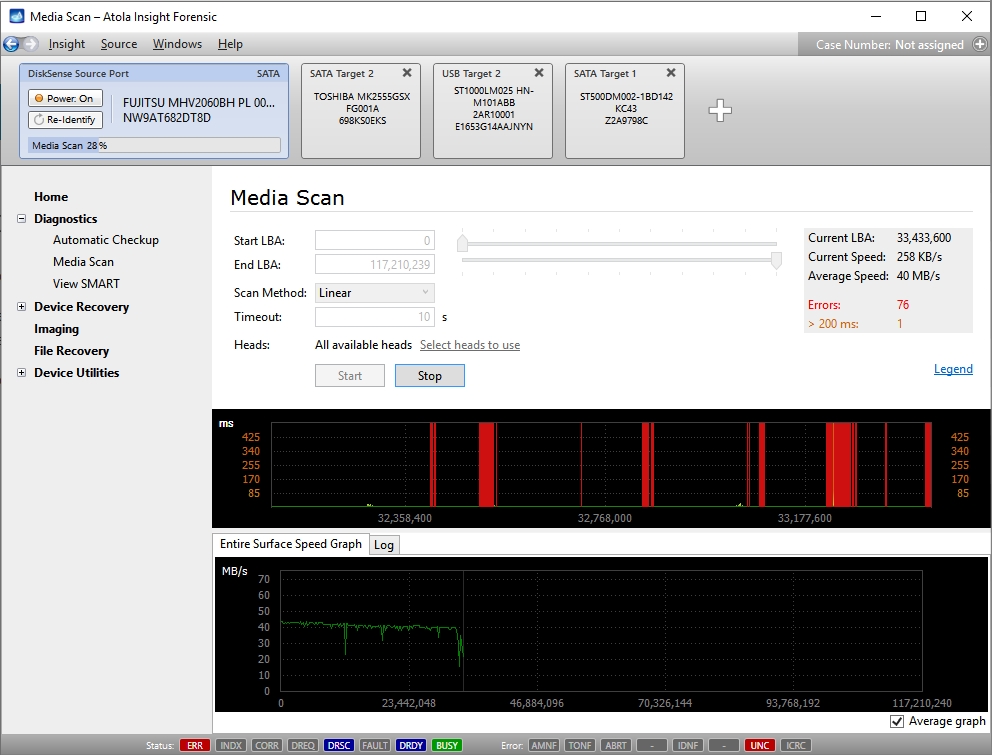
Media Scan
Media scan can help detect two kind of hard drive damage:
- Head stack damage
- Read errors ("bad sectors")
Media scan can also be used to determine general condition of the hard drive's surface.
There are three methods of scanning:
- Linear — from start LBA to end LBA.
- Backward — from end LBA to start LBA (in reverse).
- Fast — from start LBA to end LBA. Please note that in this mode the software skips large numbers of sectors; this mode is to be used only to get a quick overview of the entire surface.
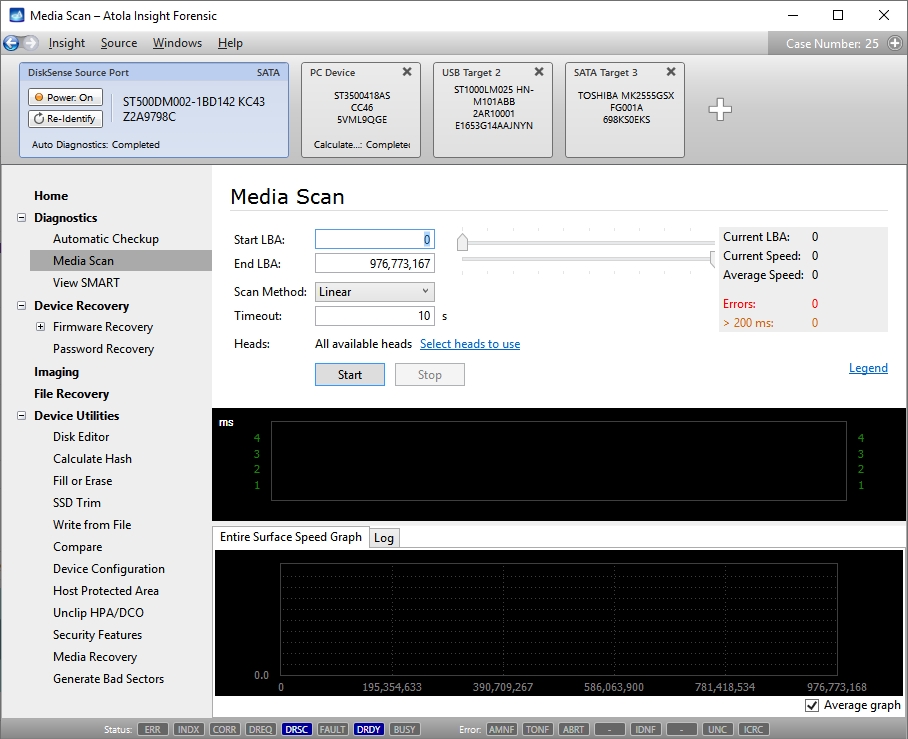
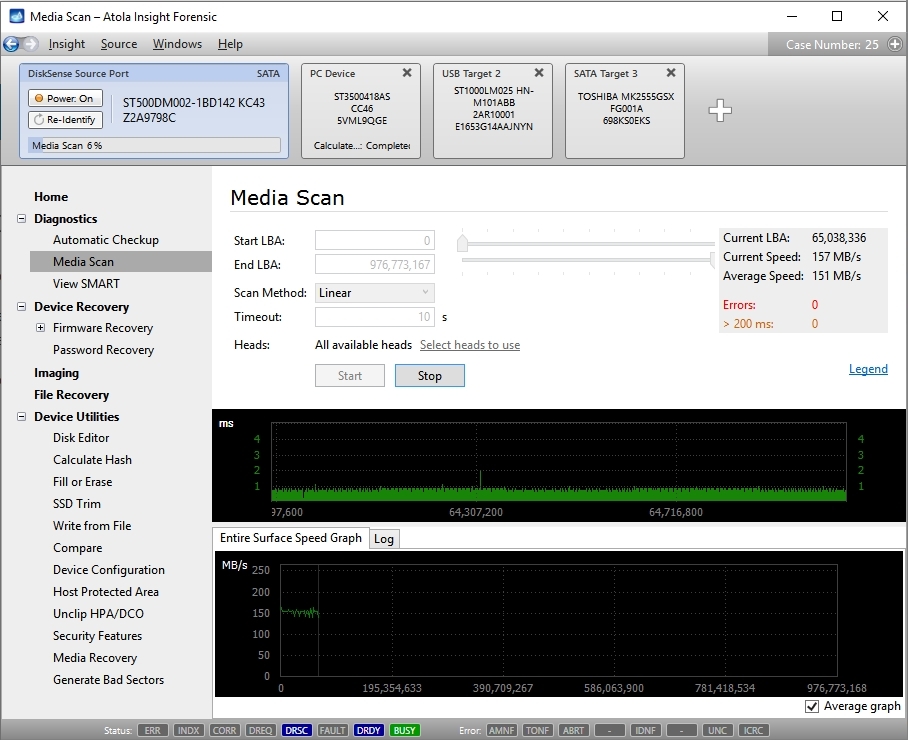
Let's scan a good hard drive and see what we get.
Good hard drive
There are two graphs; the top graph represents single block read time (one block is 2048 sectors which equals to 1 megabyte), and the bottom graph represents read speed for the entire surface.
Now let's have a look at some graphs taken from damaged hard drives.
Unstable hard drive
We call such hard drives "unstable". They usually do not have read errors, but at the same time media access times are very high and change sporadically. In most cases it is possible to create a clean image of such drive.
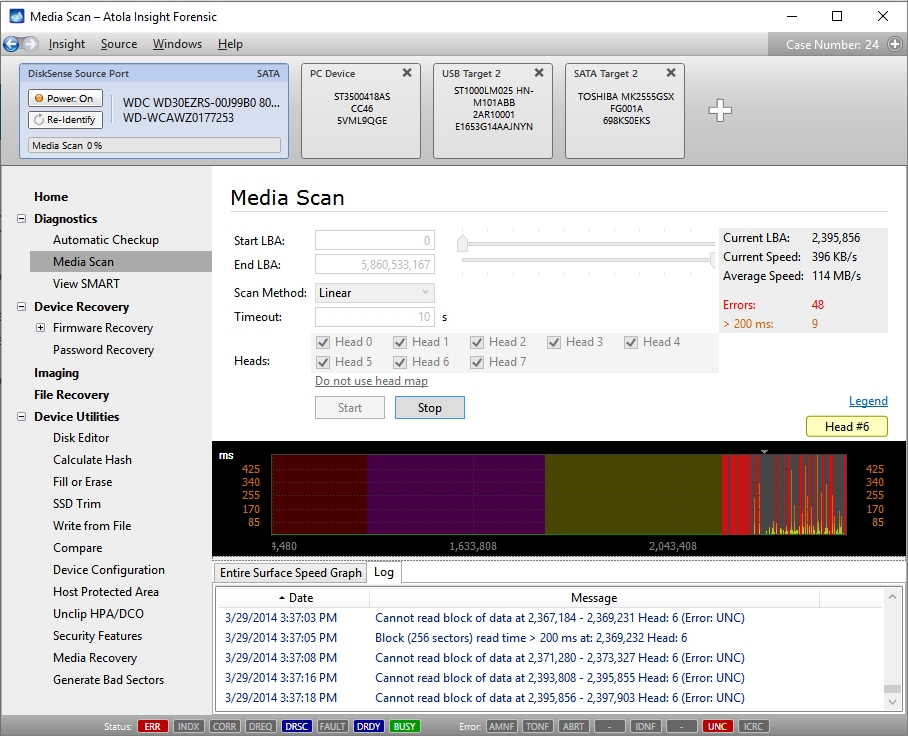
Hard drive with damaged head
You can observe patterns of delays which indicate head damage. However, please note that although the head is damaged, it can still read some sectors without errors, therefore it is possible to create a relatively good image of such hard drive by imaging data off good heads first, and then off the bad head.
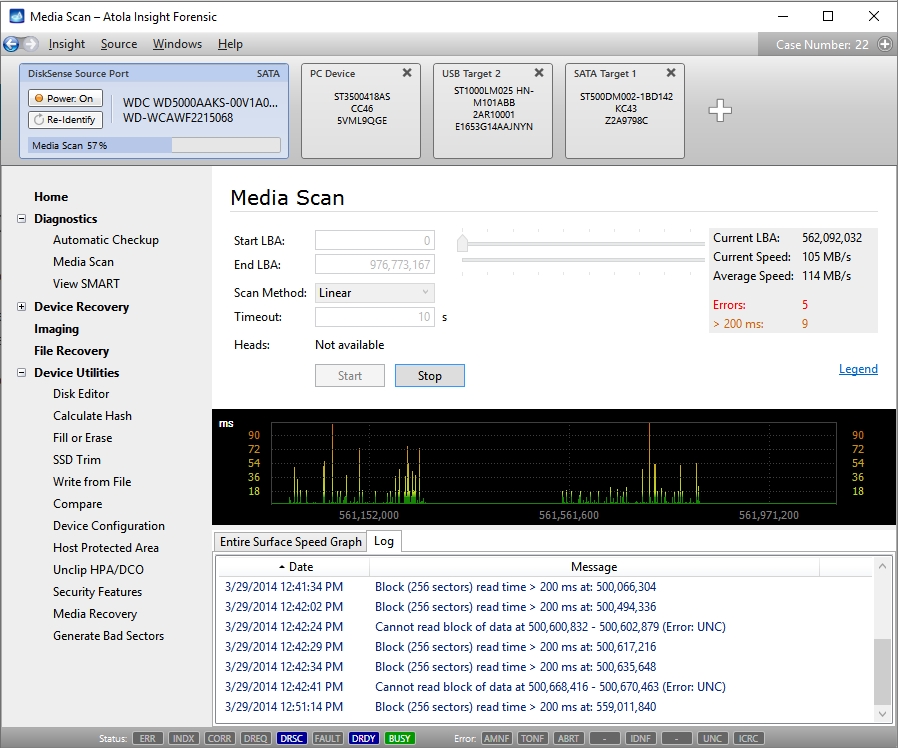
Read errors
Read errors are displayed as vertical red bars. Please note that when scanning, Atola Insight Forensic shows the entire block as bad even when only one sector in that block is damaged.